Antiviral function of IFITM proteins(engl. Wikipediateksti):
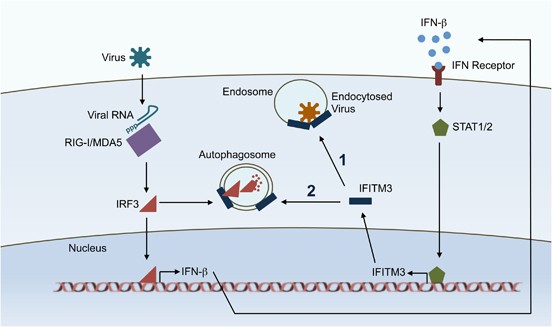
By using genomic screening for cellular factors which are involved in influenza A virus life cycle such as entry, replication and release, IFITM proteins have been identified as antiviral restriction factors for influenza A virus replication. Knockout IFITM3 increased influenza virus A replication and overexpression IFITM3 inhibits influenza virus A replication.[9] In addition to replication competent influenza A virus, IFITM proteins were able to inhibit retrovirus based pseudotyped influenza A virus, indicating that IFITM protein inhibit influenza A virus at the early step of life cycle, may occur in the entry and fusion steps.IFITM proteins also are able to inhibit several other enveloped viruses infection that belong to different virus families. These virus include flaviviruses (dengue virus and West Nile virus), filoviruses (Marburg virus and Ebola virus) coronaviruses (SARS coronavirus) and lentivirus (Human immunodeficiency virus).[10] However, IFITM proteins did not affect alphaviruses, arenaviruses and murine leukaemia virus infection.
Potential mechanisms.IFITM proteins inhibit viral membrane and cellular endosomal or lyso¬somal vesicles membrane fusion by modify lipid components or fluidity. IFITM proteins blocked the creation of hemifusion between viral membrane and cellular membrane. Furthermore, IFITM proteins reduced membrane fluidity and affected membrane curvature to restrict viral membrane fusion with the cellular membrane.[11] In addition, IFITM3 interacted with the cellular cholesterol regulatory proteins Vesicle-membrane-protein-associated protein A (VAPA) and oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) to induce intracellular cholesterol accumulation, which in turn blocked viral membrane and vesicles membrane fusion.[12]
Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar