MIKÄ ON ASFI-virus? Se on afrikansian kuumevirus ja aiheuttaa verenvuotokuumetta ja johtaa korkeaan kuolleisuuteen porsaissa. tauti ei tartu ihmisiin. Viruksest löytyy 548 hakuvastausta PubMed kirjqastosta: Paljon uusia tutkimuskai tältä vuodelta.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=ASFV
Wikipediasta ainakin löytää jotain tietoa englanniksi. Liitän sitaatin tähän blogiin, koska en ole tästä virukssta aiemmin lukenut mitään.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/African_swine_fever_virus
Evira (Elintarvikevirasto) antaa luetteloa teistä, joista tätä virusta voi päästä leviämään Suomeen. Turismi on yksi syy. Myös elintarvikeimport. Sitäpaitsi pehmeät punkit voivat kuljettaa sitä toimien vektorina
https://www.evira.fi/elaimet/elainten-terveys-ja-elaintaudit/elaintaudit/siat/afrikkalainen-sikarutto/ala-tuo-afrikkalaista-sikaruttoa-suomeen/
Asfivirus, ASFV, on ds-DNA- virus, joka replikoituu solun sytoplasmassa ja kuuluu sukuun
ASFARVIRIDAE Se infektoi porsaita, pahkasikaa, ja pensassikaa sekä Ornithoros-punkkia. ASFV onkin ainoa dsDNA virus joka käyttää vektorina arthropodaa.. Virus aiheuttaa sikakarjan porsiassa verenvuotokuumetta. Jotkut virusisolaatit ovat viikossa tappavia, mutta muissa eläinlajeissa infektio ohittuu ilman ilmeista tautia. Sub-saharan alueella virus on endeeminen ja kiertää luonnossa sykliään vektoripunkin ja willisikojen, pensassikojen ja pahkasikojen porsaiden välillä. Tauti ilmeni ensikertaa kun eurooppalaiset asukkaat toivat possuja viruksen endeemiselle alueelle ja sen takia tauti on hälyttävästi leviämässä oleva infektiotauti,
emerging infectious disease.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/African_swine_fever_virus
African swine fever virus (
ASFV) is the causative agent of African swine fever (ASF). The virus causes a
haemorrhagic fever with high mortality rates in pigs, but persistently infects its natural hosts, warthogs, bushpigs, and soft ticks of the
Ornithodoros genus, with no disease signs.
[1]
ASFV is a large, double-stranded
DNA virus which replicates in the
cytoplasm of infected cells, and is the only member of the
Asfarviridae family.
[2] ASFV infects domestic
pigs,
warthogs and
bushpigs, as well as soft
ticks (
Ornithodoros), which likely act as a
vector.
[1]
ASFV is the only known virus with a double-stranded DNA genome transmitted by
arthropods.
The virus causes a lethal haemorraghic disease in domestic pigs. Some
isolates can cause death of animals within as quickly as a week after
infection. In all other species, the virus causes no obvious disease.
ASFV is endemic to
sub-Saharan Africa
and exists in the wild through a cycle of infection between ticks and
wild pigs, bushpigs, and warthogs. The disease was first described after
European settlers brought pigs into areas endemic with ASFV and, as
such, is an example of an '
emerging infectious disease'.
ASFV -virus on ikosahedrinen ja lineaarissa genomissa on vähintään 150 geeniä. Viruksessa on piirteitä muista isoista dsDNA-viruksista kuten isorokosta, indoviruksesta ja mimiviruksesta. Replikaatio tapahtuu kohdesoluissa monosyyteissä ja makrofageissa. Viruksen pääsytapa soluun on vielä selvittämättä.
Virology
Diagram of ASFV and other members of Asfarviridae
ASFV is a large, icosahedral, double-stranded
DNA virus with a linear
genome containing at least 150 genes. The number of genes differs slightly between different isolates of the virus.
[3] ASFV has similarities to the other large DNA viruses, e.g.,
poxvirus,
iridovirus, and
mimivirus. In common with other
viral haemorrhagic fevers, the main target cells for replication are those of
monocyte,
macrophage
lineage. Entry of the virus into the host cell is receptor-mediated,
but
the precise mechanism of endocytosis is presently unclear.
[4]
The virus encodes enzymes required for replication and transcription
of its genome, including
elements of a base excision repair system,
structural proteins, and many proteins that are not essential for
replication in cells, but instead have roles in virus survival and
transmission in its hosts.
Virus replication takes place in perinuclear
factory areas. It is a highly orchestrated process with at least four
stages of transcription—immediate-early, early, intermediate, and late.
The majority of replication and assembly occurs in discrete, perinuclear
regions of the cell called virus factories, and finally progeny virions
are transported to the plasma membrane along
microtubules where they
bud out or are
propelled away along
actin
projections to infect new cells. As the virus progresses through its
lifecycle, most if not all of the host cell's organelles are modified,
adapted, or in some cases destroyed.
Macrophage cell in early stages of infection with ASFV
Assembly of the icosahedral
capsid occurs on modified membranes from the
endoplasmic reticulum. Products from proteolytically processed polyproteins form the core shell between the internal membrane and the
nucleoprotein core.
An additional outer membrane is gained as particles bud from the
plasma membrane.
The virus encodes proteins that inhibit signalling pathways in infected
macrophages and thus modulate transcriptional activation of
immune response genes. In addition, the virus encodes proteins which inhibit
apoptosis of infected cells to facilitate production of progeny virions. Viral membrane proteins with similarity to cellular
adhesion proteins modulate interaction of virus-infected cells and extracellular virions with host components.
[2]
Genotypes
Based on sequence variation in the C-terminal region of the
B646L gene encoding the major capsid protein p72, 22 ASFV genotypes (I–XXII) have been identified.[5]
All ASFV p72 genotypes have been circulating in eastern and southern
Africa. Genotype I has been circulating in Europe, South America, the
Caribbean, and western Africa. Genotype VIII is confined to four East
African countries.
Evolution
The virus is thought to be derived from a virus of soft tick (genus
Ornithodoros) that infects wild swine, including
giant forest hogs (
Hylochoerus meinertzhageni), warthogs (
Phacochoerus africanus), and bushpigs (
Potamochoerus porcus).
[6] In these wild hosts, infection is generally asymptomatic. This virus appears to have evolved around
1700 AD.
This date is corroborated by the historical record. Pigs were initially domesticated in North Africa and Eurasia.
[7]
They were introduced
into southern Africa from Europe and the Far East
by the Portuguese (300 years ago) and Chinese (600 years ago),
respectively.
[8] At the end of the 19th century, the extensive
pig industry in the native region of ASFV (
Kenya) started after massive losses of cattle due to a
rinderpest outbreak.
Pigs were imported on a massive scale for breeding by colonizers from
Seychelles in 1904 and from
England in 1905. Pig farming was free-range at this time.
The first outbreak of ASF was reported in 1907.
Signs and symptoms
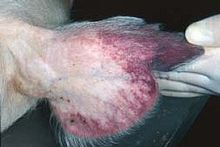
Reddening of the ears is a common sign of African swine fever in pigs.
In the acute form of the disease caused by highly virulent strains,
pigs may develop a high fever, but show no other noticeable symptoms for
the first few days.
[9] They then gradually lose their appetites and become depressed. In
white-skinned pigs,
the extremities turn blueish-purple and hemorrhages become apparent on
the ears and abdomen. Groups of infected pigs lie huddled together
shivering, breathing abnormally, and sometimes coughing. If forced to
stand, they appear unsteady on their legs. Within a few days of
infection, they enter a comatose state and then die. In pregnant sows,
spontaneous abortions occur. In milder infections, affected pigs lose
weight, becoming thin, and develop signs of pneumonia, skin ulcers, and
swollen joints.
[10]
Diagnosis
The clinical symptoms of ASFV infection are very similar to classical swine fever virus, and the two diseases normally have to be distinguished by laboratory diagnosis. This diagnosis is usually performed by an
ELISA or isolation of the virus from either the blood, lymph nodes, spleen, or serum of an infected pig.
[10]
History
The swelling around the kidneys and the muscle hemorrhages visible here are typical of pigs with African swine fever.
The first outbreak was retrospectively recognized as having occurred in 1907 after ASF was first described in 1921 in Kenya.
[11] The disease remained restricted to Africa until 1957, when it was reported in
Lisbon,
Portugal.
A further outbreak occurred in Portugal in 1960. Subsequent to these
initial introductions, the disease became established in the Iberian
peninsula, and sporadic outbreaks occurred in
France,
Belgium, and other European countries during the 1980s. Both
Spain and
Portugal had managed to eradicate the disease by the mid-1990s through a slaughter policy.
[12]
Cuba
In 1971 an
outbreak of the disease occurred in Cuba, resulting in the slaughter of
500,000 pigs to prevent a nationwide animal epidemic. The outbreak was
labeled the "most alarming event" of 1971 by the United Nations Food and
Agricultural Organization.
Conspiracy theory
Six years after the event the newspaper
Newsday, citing untraceable sources,
[13][14] claimed that with at least the tacit backing of U.S.
Central Intelligence Agency officials, operatives linked to anti-Castro
terrorists allegedly introduced African swine fever virus into
Cuba
six weeks prior to the outbreak in 1971, for the purposes of
destabilizing the Cuban economy and encouraging domestic opposition to
Fidel Castro.
The virus was allegedly delivered to
the terrorists from an army base
in the Panama Canal Zone by an unnamed U.S. intelligence source.
[15][16]
The Caribbean
ASFV crossed the
Atlantic Ocean, and outbreaks were reported in some Caribbean islands, including the
Dominican Republic. Major outbreaks of ASF in Africa are regularly reported to the World Organisation for Animal Health (previously called
L'office international des épizooties).
Eastern and Northern Europe
Outside Africa, an outbreak occurred at the beginning of 2007 in
Georgia, and subsequently spread to
Armenia,
Azerbaijan,
Iran,
Russia, and
Belarus, raising concerns that ASFV may spread further geographically and have negative economic effects on the swine industry.
[12][17][18]
In August 2012, an outbreak of African swine fever was reported in
Ukraine.
[19] In June 2013, an outbreak was reported in
Belarus.
[20]
African swine fever had become 'endemic' in the Russian Federation
since spreading into the North Caucasus 'in November 2007, most likely
through movements of infected wild boar from Georgia to (Chechnya)',
said a 2013 report by the Food and Agriculture Organization, a
United Nations agency.
[21]
The report showed how the disease had spread north from the Caucasus to
other parts of the country where pig production was more concentrated
the
Central Federal District (home to 28.8% of Russia's pigs) and the
Volga Federal District
(with 25.4% of the national herd) and northwest towards Ukraine,
Belarus, Poland and the Baltic nations. In Russia, the report added,
the
disease was 'on its way to becoming endemic in
Tver oblast'
(about 106 km north of Moscow—and about 500 km east of Russia's
littoral neighbours on the Baltic. Among the vectors for the spread in
Russia of African swine fever virus was the 'distribution' of 'infected
pig products' outside affected (quarantined and trade restricted) areas,
travelling large distances (thousands of kilometers) within the
country.
'Wholesale buyers, particularly the military food supply system, have
been implicated multiple times in the illegal distribution of
contaminated meat' were vectors for the virus's spread, said the Food
and Agriculture Organization report—and evidence of that was 'repeated
outbreaks in
Leningrad oblast'. The report warned that 'countries immediately bordering the
Russian Federation, particularly
Ukraine,
Moldova,
Kazakhstan and
Latvia,
are most vulnerable to [African swine fever] introduction and endemic
establishment, largely because the
biosecurity of their pig sector is
predominantly low.
Preventing the spread of [African swine fever] into
Ukraine is particularly critical for the whole pig production sector in
Europe.
Given the worrisome developments in the Russian Federation,
European countries have to be alert. They must be ready to prevent and
to react effectively to [African swine fever] introductions into their
territories for many years to come'...To stop the virus's spread, 'the
current scenario in the Russian Federation suggests that [prevention]
should be particularly stressed at the often informal backyard level and
should involve not just pig keepers, but all actors along the whole
value chain—butchers, middlemen, slaughterhouses, etc...They need to be
aware of how to prevent and recognize the disease, and must understand
the importance of reporting outbreaks to the national authorities...It
is particularly important that [African swine fever]-free areas remain
free by preventing the [re]introduction of the disease and by swiftly
responding to it when it occurs'.
In January 2014, authorities announced the presence of African swine fever in Lithuania and Poland,[22] in June 2014 in Latvia, and in July 2015 in Estonia.[23]
Estonia in July 2015 recorded its first case of African swine fever in farmed pigs in
Valgamaa county on the country's border with Latvia. Another case was reported same day in
Viljandi county, which also borders Latvia. All the pigs were culled and their carcasses incinerated.
[24]
Less than a month later, almost 15,000 farmed pigs had been culled and
the country was 'struggling to get rid of hundreds of tons of
carcasses'. The death toll was 'expected to rise'.
[25]
Latvia in January 2017 declared African swine fever emergency in
relation to outbreaks in three regions, including a pig farm in
Krimulda region, that resulted in a cull of around 5,000 sows and piglets by using gas.
[26][27] In February another massive pig cull was required, after an industrial scale farm of the same company in
Salaspils region was found infected, leading to a cull of about 10,000 pigs.
[28]
Czech republic in June 2017 recorded its historically first case of African swine fever.
[29]
Alternative theory
The appearance of ASF outside Africa at about the same time as the emergence of
AIDS led to some interest in whether the two were related, and a report appeared in
The Lancet supporting this in 1986.
[30] However, the realization that the human immunodeficiency virus (
HIV) causes
AIDS, discredited any potential connection with ASF.
See also
- Animal viruses
- Oma kommentti. Mitä tulee sian kasvatukseen ja sianlihan syömiseen, olen samaa mieltä kuin Mooseksen laki. Jalostetut possut ja siat ovat immuniteetiltään heikompia kuin luonnolliset vastineet ja suuri määrä tekee niistä vain ihmiskuntaan iskevien viruksien kiertoon ison soveltuvan altaan.
- Miksi niitä sitten on olemassa, arvelen että kudoksensiirtotarkoituksiin, koska kudos on lähellä ihmisen kudosta. ja insuliinin tekoa varten, ehkä muitakin erityisiä kudoksia tai molekyylejä voidaan hyödyntää vaikka semisynteeseihin.
- On periaate allergioissa että jos jotain lääkettä annetaan sekä ihon kautta , suun kautta että parenteraalisti , seuraa helposti allergisia reaktioita. Samoin jos esim käytetään sikaperäistä siirrettä tai insuliiniä ja sitten vielä tai ennen sitä syödään sikaa, voidaan saada vasta-aineita siirrettä ja insuliinia kohtaan helpommin. Arvelen.
- Mitä tulee eläinten teurastukseen, en ole vastaan seemiläisten tuhatvuotista perinnettä, jossa veren määrää kudoksessa saadaan laskemaan erittäin tehokkaasti , sillä veressä voi olla paljon ihmiselle epäsuotuisia tekijöitä jos sitä jää hajoamaan kudokseen
- Mitä tulee Pietarin taivaalliseen näkyyn kaikenlaisesta ravinnosta, siinä ei mainittu possuja. muta tässä en käy saivartelemaan, sanoinpa vain mikä on mielestäni ihmiskuntamitassa terveellistä, toisaalta ihmiskunnassa on paljon animaalisen proteiinin puutetta,
- Tässä olen vain teoretisoinut Mooseksen lain kohdan mahdollista merkitystä, kun kielletään syömästä sikaa.
- (Lampaan ja vuohen aksvatus voisi olla hyvä korvike ja varsinkin jos lampailla on kontrolloitua laidunta ja vihreää rrehua , nekin pysyvät terveinä paremmin kuin enenn vanhaan)